Insulation
The higher the number the more sustainable and “green” the material
- Is there enough material so that we can continue to use it at the present rate… Is the present use sustainable? 34%
- Is the present use having little or no impact on the environment including destruction of habitat and CO2 release 13%
- Ability for the Material to be Harmlessly Returned to Nature 18%
 Insulation Description
Insulation Description
Building insulation refers broadly to any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation (e.g. for vibrations caused by industrial applications). Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.
Thermal insulation in buildings is an important factor to achieving thermal comfort for its occupants. Insulation reduces unwanted heat loss or gain and can decrease the energy demands of heating and cooling systems. It does not necessarily deal with issues of adequate ventilation and may or may not affect the level of sound insulation. In a narrow sense insulation can just refer to the insulation materials employed to slow heat loss, such as: cellulose, glass wool, rock wool, polystyrene, urethane foam, vermiculite, perlite, wood fibre, plant fibre (cannabis, flax, cotton, cork, etc.), recycled cotton denim, plant straw, animal fibre (sheep’s wool), cement, and earth or soil, Reflective Insulation (also known as Radiant Barrier) but it can also involve a range of designs and techniques to address the main modes of heat transfer – conduction, radiation and convection materials. Many of the materials in this list deal with heat conduction and convection by the simple expedient of trapping large amounts of air (or other gas) in a way that results in a material that employs the low thermal conductivity of small pockets of gas, rather than the much higher conductivity of typical solids. (A similar gas-trapping principle is used in animal hair, down feathers, and in air-containing insulating fabrics).
The effectiveness of Reflective Insulation (Radiant Barrier) is commonly evaluated by the Reflectivity (Emittance) of the surface with airspace facing to the heat source.
The effectiveness of bulk insulation is commonly evaluated by its R-value, of which there are two – metric (SI) and US customary, the former being 0.176 times the latter. For attics, it is recommended that it should be at least R-38 (US customary, R-6.7 metric). However, an R-value does not take into account the quality of construction or local environmental factors for each building. Construction quality issues include inadequate vapor barriers, and problems with draft-proofing. In addition, the properties and density of the insulation material itself is critical.
Types of Insulation
- Cellulose Insulation
- CFCs
- Agricultural Fiber
- Foam
- Perlite
- Rockwool
- Spray foams (coming soon)
- Sheep wool (coming soon)
- Cotton Insulation
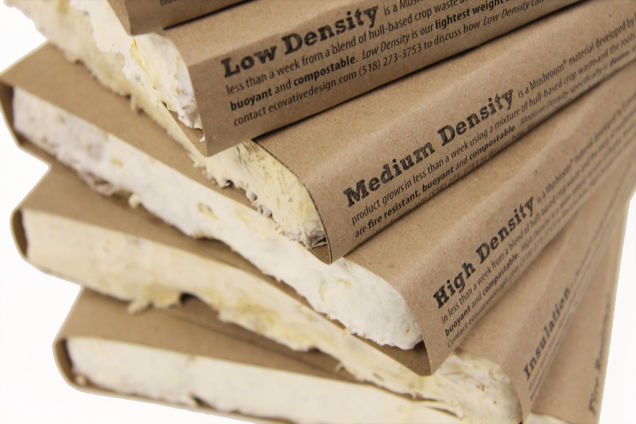
Mycelium or Mushroom Insulation
Grow-In-Place Mushroom® Insulation R 3.6 per inch
Mushroom Insulation Tiny House Video
Click Image Below See More Building Materials and Their Sustainability